According to Worldometer’s current data, the world’s population stands at an impressive 7.8 billion and is on a steady incline. The World Bank projects that by 2050, this figure will soar to approximately 9.7 billion, and by the end of the 21st century, it could reach 11.2 billion. Such exponential growth underscores an inevitable surge in food demand, posing significant challenges and opportunities for the agriculture sector.
Advancements in Agricultural Technology
In response to the escalating demand for food, the agricultural industry is turning to innovative solutions. The sector is increasingly incorporating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and various automation technologies to enhance production capabilities. These advanced technologies are essential for meeting the growing global demand for food efficiently and sustainably.
Challenges in Agriculture: The Road to Sustainability
The agricultural industry, with its expansive scale and complexity, faces a myriad of challenges that threaten its sustainability and long-term viability. One of the most significant challenges is the reliance on labor-intensive practices, which are not only physically demanding but also face a shortage of skilled labor. This reliance hinders efficiency and increases the vulnerability of the sector to workforce fluctuations.
Moreover, the pressures of a competitive market pose another substantial challenge. Farmers and agricultural businesses must constantly adapt to changing market demands, fluctuating prices, and the evolving preferences of consumers. This constant need for adaptation can strain resources and impact the profitability and sustainability of agricultural operations. Environmental concerns are another critical aspect impacting agriculture. Practices that lead to soil degradation, water scarcity, and the loss of biodiversity are unsustainable in the long term. The industry must balance the need for high productivity with environmentally friendly practices to ensure its future.
Additionally, the agricultural sector is often affected by unpredictable factors like weather conditions, pests, and diseases. These factors can drastically impact crop yields and quality, adding to the industry’s uncertainties and challenges. Supply chain complexities further complicate matters. From farm to table, numerous steps are involved, including harvesting, processing, transportation, and distribution. Each step presents its own set of challenges, such as logistical inefficiencies, food safety concerns, and the loss of produce quality.
To address these challenges, the agricultural industry needs to adopt innovative approaches, integrating technology and sustainable practices. This can include precision farming, sustainable resource management, and the development of resilient supply chains. Embracing such changes is crucial to ensure the industry’s survival and growth, meeting the global demand for food without compromising the planet’s health and resources.
The Role of Blockchain in Agriculture
Blockchain technology emerges as a key player in addressing and managing the foreseeable risks within the agriculture and food sector. It offers a pathway to maintaining affordability and sustainability throughout the industry. Here are some insights into the role and forecast of blockchain in agriculture:
Market Growth and Projections
The blockchain technology in the food and agriculture sector is experiencing rapid growth and expansion, as evidenced by significant market value increases. In 2017, the sector’s global market value stood at approximately $32.2 million, a figure that’s projected to soar to around $1.4 billion by 2028. This remarkable growth trajectory highlights the increasing recognition of blockchain’s potential in transforming the agriculture and food industries.
A 2021 report by Reportlinker.com on ‘Blockchain In Agriculture And Food Supply Chain’ further underlines this trend. The report noted a substantial increase in the market, from $128.87 million in 2020 to $189.48 million in 2021. This rapid growth, calculated at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 47%, signifies the burgeoning interest and investment in blockchain technology within these sectors.
The same report projects that the market will continue its upward trend, reaching an estimated $886.18 million by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 47.1%. This consistent growth rate is a clear indication of the transformative impact blockchain technology is expected to have on agriculture and food supply chains.
Blockchain technology offers a range of benefits in these sectors, including enhanced traceability of food products, improved supply chain efficiency, and increased transparency in agricultural transactions. These advantages are crucial in addressing some of the pressing challenges in the food and agriculture sector, such as food fraud, safety concerns, and inefficiencies in supply chain management. The substantial investments and projected growth in blockchain technology within the food and agriculture sector are a testament to its potential in revolutionizing these industries. As blockchain continues to evolve, it’s poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of food production, distribution, and consumption on a global scale.
Understanding Blockchain in Agriculture
Blockchain agriculture refers to the application of blockchain technology within the agricultural sector to enhance operations and achieve profitable outcomes. This includes sustainable business practices, waste reduction, informed consumer purchasing, and secure, fraud-free transactions. The emergence of ‘Smart Agriculture’ incorporates ICTs, blockchain, and other technologies to manage natural resources efficiently and reduce environmental impact.
Applications of Blockchain in Agriculture
- Enhancing Farm Inventory Management. Many farming organizations currently struggle with advanced technology for inventory management, leading to waste and financial losses. Blockchain can revolutionize this aspect by monitoring storage conditions and product expiry, allowing for timely intervention;
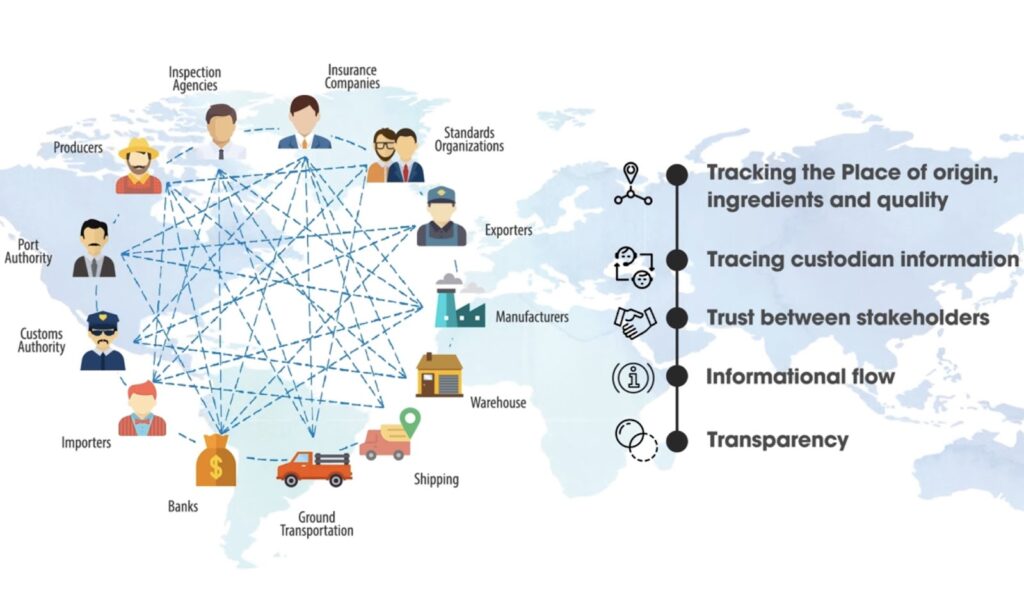
- Supply Chain Efficiency. Blockchain technology is poised to be a game-changer in transforming the agricultural supply chain, particularly for small to mid-sized farmers who often find themselves at a technological disadvantage. The introduction of a blockchain ledger system in the agricultural domain can serve as a cornerstone for numerous efficiency improvements and cost reductions. This technology offers a decentralized and transparent platform that can streamline the entire supply chain process, from farm to table.
For smaller farmers, the impact of blockchain can be especially transformative. These farmers frequently grapple with limited resources and access to advanced technological solutions, which can hamper their production efficiency and market competitiveness. By integrating blockchain, they gain access to a system that offers real-time tracking of products, automated transactions, and a transparent record of all activities. This visibility can significantly reduce the time and resources spent on manual record-keeping and transaction processing.
Moreover, blockchain’s inherent attributes, such as data immutability and traceability, enhance the reliability of the supply chain. It allows farmers to prove the authenticity and quality of their produce, enabling them to negotiate better prices and access new markets. The reduced overheads from streamlined operations and the potential for higher market returns can collectively boost the overall production efficiency of small and mid-sized farms.
In essence, blockchain technology has the potential to level the playing field for smaller agricultural players, providing them with tools and capabilities that were previously accessible only to larger, more technologically advanced operations. Its adoption in the agricultural supply chain could usher in a new era of efficiency, transparency, and fairness, benefitting not only farmers but the entire agricultural ecosystem.
Farm Management Software Modernization
Integrating blockchain with farm management software can elevate these systems to new heights, offering enhanced security and protection against cyber threats.
- IoT Security Optimization. Blockchain can also bolster the security of IoT devices used in agriculture, protecting them from cyber vulnerabilities and enhancing their network functionality;
- Fair Pricing and Microloans. Blockchain technology is significantly reshaping the agricultural landscape, particularly in how it facilitates fair pricing and financial accessibility for farmers, especially those who operate on a smaller scale. This technology’s ability to provide transparency and trust in transactions ensures that farmers receive a fair price for their produce, addressing a long-standing issue in the agricultural supply chain.
Traditionally, small and mid-sized farmers have faced challenges in getting fair compensation for their produce due to a lack of transparency and market data, and the dominance of intermediaries in the supply chain. Blockchain technology disrupts this dynamic by enabling a direct connection between farmers and buyers. This direct connection not only reduces the reliance on intermediaries but also ensures that farmers have more control over the pricing of their products. The immutable nature of blockchain records means that all parties have access to the same information regarding the quality, origin, and journey of the produce, which helps in establishing fair pricing based on factual data.
Furthermore, blockchain opens up new avenues for small and mid-sized farmers in terms of financial support. Access to credit is a significant hurdle for many farmers, who often face high-interest rates and stringent requirements from traditional banking institutions. Blockchain technology facilitates the provision of microloans, offering a more accessible and flexible source of funding. Through decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, farmers can connect with a global pool of lenders, enabling them to secure loans with more manageable interest rates and terms. This financial accessibility is crucial in helping them cover operational costs, invest in improvements, and ultimately, sustain and grow their businesses.
Blockchain technology’s role in ensuring fair pricing and improving access to financial resources represents a major stride towards economic empowerment and sustainability for small and mid-sized farmers. By democratizing access to markets and finance, blockchain is not just a technological innovation but a catalyst for social and economic change in the agricultural sector. Its continued adoption and development promise a more equitable and resilient future for farmers worldwide.
Blockchain’s Impact on Food Security
Blockchain technology’s ability to consolidate and transparently present information is revolutionizing the agricultural sector, especially in the realms of seed quality, crop growth, and the journey of produce from farm to consumer. This transparent data management is critical in fostering ethical and sustainable production and distribution practices in agriculture.
For seed quality, blockchain can store and verify data regarding the origin of seeds, their genetic makeup, and the conditions under which they were cultivated. This information is vital for farmers who aim to cultivate high-quality crops, as it ensures that the seeds they use meet certain standards of purity and genetic integrity. Moreover, this transparency helps in protecting against counterfeit seeds, a major issue in some agricultural markets. In terms of crop growth, blockchain can track and record various factors such as soil quality, water usage, fertilizer application, and pest control methods. This data provides insights into the environmental impact of farming practices and helps in optimizing crop yield and quality. By having access to this information, farmers can make more informed decisions, leading to more sustainable and efficient farming practices.
When it comes to the journey of produce from farm to consumer, blockchain offers unparalleled traceability. It can track each step of the supply chain in real time, from harvesting, processing, and packaging to transportation and retail. Consumers increasingly demand transparency about where their food comes from and how it is produced, and blockchain technology meets this need by providing a clear, unalterable record of the entire journey of produce. This level of traceability is essential in ensuring food safety, preventing food fraud, and promoting ethical sourcing practices.
Blockchain’s capacity to consolidate and transparently share information across the agricultural supply chain not only builds trust among consumers but also encourages more responsible and sustainable agricultural practices. As the technology continues to be adopted and integrated into various stages of agricultural production and distribution, it holds the promise of a more ethical, sustainable, and transparent food system.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While blockchain holds great promise, its full potential in addressing food security and supporting sustainable practices is yet to be fully realized. Challenges include ensuring decentralized implementation, digital literacy among rural populations, and integration into broader food security strategies.
Concluding Thoughts on Blockchain in Agriculture
The advent of blockchain technology in agriculture marks a pivotal turn in addressing the challenges of a rapidly growing global population and its consequent food demands. With the world population projected to reach staggering figures in the coming decades, the pressure on the agriculture sector to adapt and evolve is more critical than ever. Blockchain emerges as a beacon of hope, offering innovative solutions to enhance sustainability, efficiency, and fairness in the agricultural supply chain.
This technology’s potential to revolutionize the industry is not just theoretical but is increasingly evidenced by significant market growth and adoption. From farm inventory management to supply chain efficiency, blockchain’s applications in agriculture are manifold. It is setting a new standard in how we manage, track, and verify agricultural products, from the seed’s origin to the consumer’s table. The enhanced transparency and security provided by blockchain ensure that every stakeholder in the agricultural ecosystem, especially small and mid-sized farmers, can operate on a level playing field.
Moreover, blockchain’s role in optimizing IoT security, enabling fair pricing, and facilitating accessible microloans represents a holistic approach to tackling the multifaceted challenges of modern agriculture. However, to fully harness its benefits, we must navigate challenges such as digital literacy among rural populations and the integration of this technology into broader food security strategies.
In summary, blockchain technology stands not just as a tool for innovation but as a catalyst for a more sustainable, equitable, and efficient agricultural future. Its growing adoption and market potential underscore its critical role in reshaping the agricultural landscape to meet the demands of a burgeoning global population, offering a promising outlook for food security and sustainable farming practices worldwide.